- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 6 Downloads
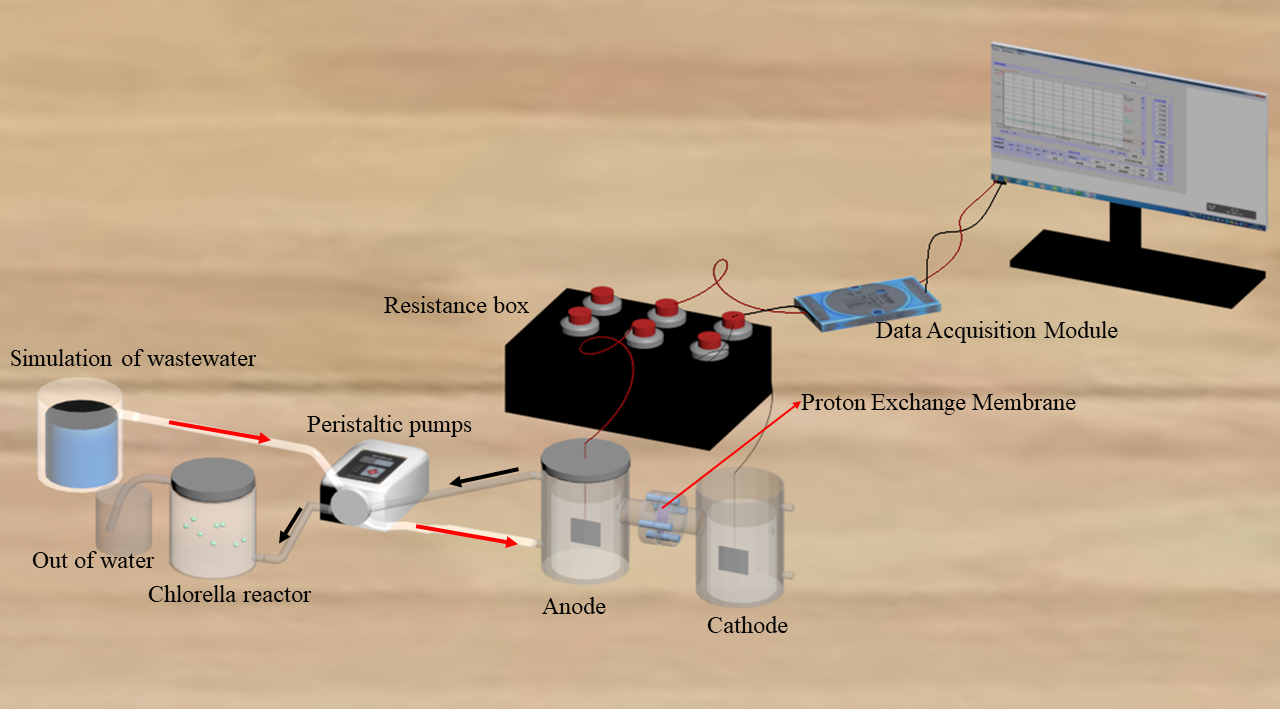
Chlorella microbial fuel cells may be an alternative technology for wastewater treatment. Using microalgae and activated sludge as raw materials, a C-MFCs was established, and the effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus ratios in the influent on the electrochemical performance of C-MFCs and the removal effect of NH3-N, COD and TP were investigated. The results show that when N:P=3:1 and the external resistance is 1000 Ω, the removal rates of NH3-N, COD and TP are 72.48±1.94%, 81.26±4.4% and 65.62%±2.14%, respectively, and the highest chlorophyll a content is 108.82 mg/L. The maximum voltage and maximum power 92.94 mV and 234.01 mW/m2. The microbial community structure in the anode chamber was analyzed and the results are as follows: At N:P=3:1, the dominant bacteria at the genus level in the anode chamber were Klebsiella (32.12%) and Prevotella (14.45%). The number of OTUs in the anode chamber changes under different N:P conditions. It can be concluded that N:P affects the power generation capacity of C-MFCs and the removal of NH3-N, COD and TP. Overall,when N:P=3:1, the C-MFCs had the best power production capacity and the removal of NH3-N, COD and TP. Regulation of N:P in aquaculture wastewater is an effective way to improve performance of C-MFCs.