- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 9 Downloads
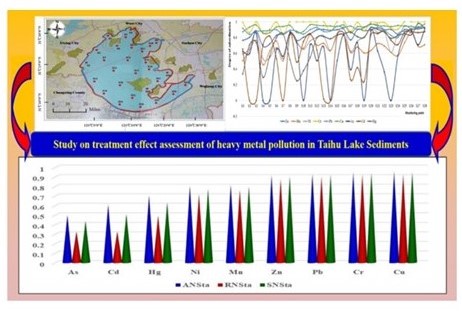
In order to explore an effective assessment method for the treatment effect of heavy metal pollution in the sediment of Taihu Lake in China, based on the research background analysis and literature review, this paper reconstructs the spatial niche suitability model and applies it to the effect assessment of heavy metal pollution treatment in Taihu Lake sediment. The study found that the pollution degree of heavy metals in Taihu Lake sediment is as follows: North water area, West water area, South water area and East water area. The assessment results of the effect of heavy metal pollution treatment in Taihu Lake sediment by using SNSM are as follows: As > Cd > Hg > Ni > Mn > Zn > Pb > Cr > Cu. The four heavy metals that pose the greatest threat to the effect of Taihu Lake sediment are As, Cd, Hg and Ni; in particular, As and Cd are carcinogenic heavy metals, which the management authorities should pay special attention to. The research results of this paper are of great significance in supporting the government to formulate relevant policies for treating Taihu Lake and helping the management departments improve the treatment effect of heavy metal pollution in Taihu Lake sediments.