- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 24 Downloads
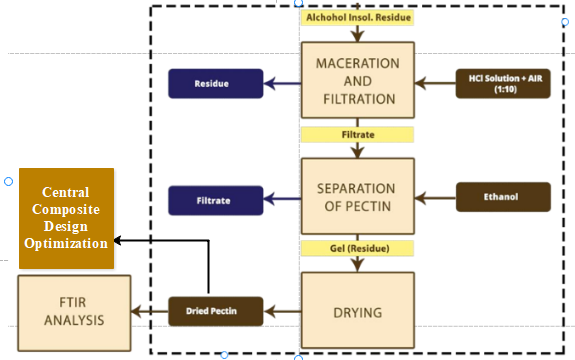
Pectin extraction from various fruits and its application in food products have been debatable issues for ages. We conducted our research on the biomass wastes of the food industry, primarily banana (Musa Acuminata) peels, in order to develop a modified procedure for the effective extraction of this substance. Banana peels were used to extract pectin using the alcohol precipitation technique. This investigation's goal is to contrast yields of pectin from ripe banana peels by varying the conditions of temperature, time, and pH. Pectin was extracted from banana peels with hydrochloric acid and a central composite design was used to determine the effects of pH (1.5–2.5), extraction temperature (40–85°C), and time (90–240 min) on the yield and purity. The provenience procedure was improved by the removal of phenols, flavonoids, fats, oils, wax, and pigments well before the extraction of pectin. It results in better purity and high yield of Pectin. Soxhlet extraction was initially used to remove them followed by maceration of Alcohol Insoluble Residue (AIR). An FTIR spectrum of the extracted pectin was compared with the commercial pectin and results are reported. Different techniques and methodology are also discussed in this study.