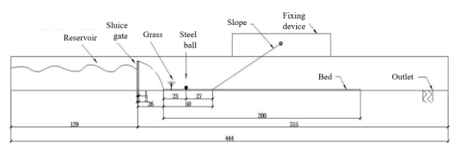
An experimental study was carried out to investigate the energy dissipation characteristics of sea grass in a dam break flume. Dam break flows were generated in a flume. A steel ball was subjected to the dam break flow, and then climbed on a slope. Artificial sea grass was used as the energy dissipation plant. In the study, the characteristics (such as wave height, wave velocity, Froude number) of the dam break flow were investigated, the ball subjected to the dam break flow was observed, some impact factors of ball climbing height were explored. Results show that, the ball climbing height increases with increasing reservoir water level and decreasing ball diameter. The relative ball climbing height decreases with increasing relative distance and increasing relative grass height. The relative ball climbing height shows logarithmic correlation with relative reservoir water level. The energy dissipation coefficient of the sea grass changed with reservoir water level, with the average value of 0.34 in this study.
Total file downloads: 7