- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 5 Downloads
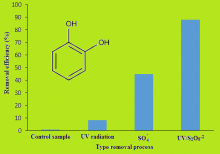
Catechol is used as an antioxidant, fungicide, and polymerization inhibitors in a variety of industries such as petrochemical. Catechol must be removed from effluents before it enters to environment. This study aimed to investigate combined UV radiation and persulfate process in removal of catechol from aqueous solutions. All experiments were performed in a batch reactor. Data analysis were done with Design of Experiment (DoE) software. The effects of various variables such as pH, initial persulfate concentration, and initial Catechol concentration were investigated. The findings indicated with increases in persulfate concentration and decrease in catechol concentrations, the removal efficiency increased. Acidic pH and UV radiation were the leading factors in removal of catechol. The optimum pH, persulfate concentration, and catechol concentration were obtained 7, 0.04 M, and 100 mg l-1, respectively. More removes of catechol was achieved in optimum conditions within contact time of 60 min. The synergic effects of UV and persulfate radical were about 88%. Approximately 60% of catechol was mineralized within contact time of 60 min. Persulfate radicals resulting from UV/S2O82- were the main effective oxidants in removal and mineralization of catechol. Owing to high removal efficiency of persulfate compounds which are, also, abundant and inexpensive, these can be applied in removal of persistent organic pollutants from aqueous solutions.