- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 16 Downloads
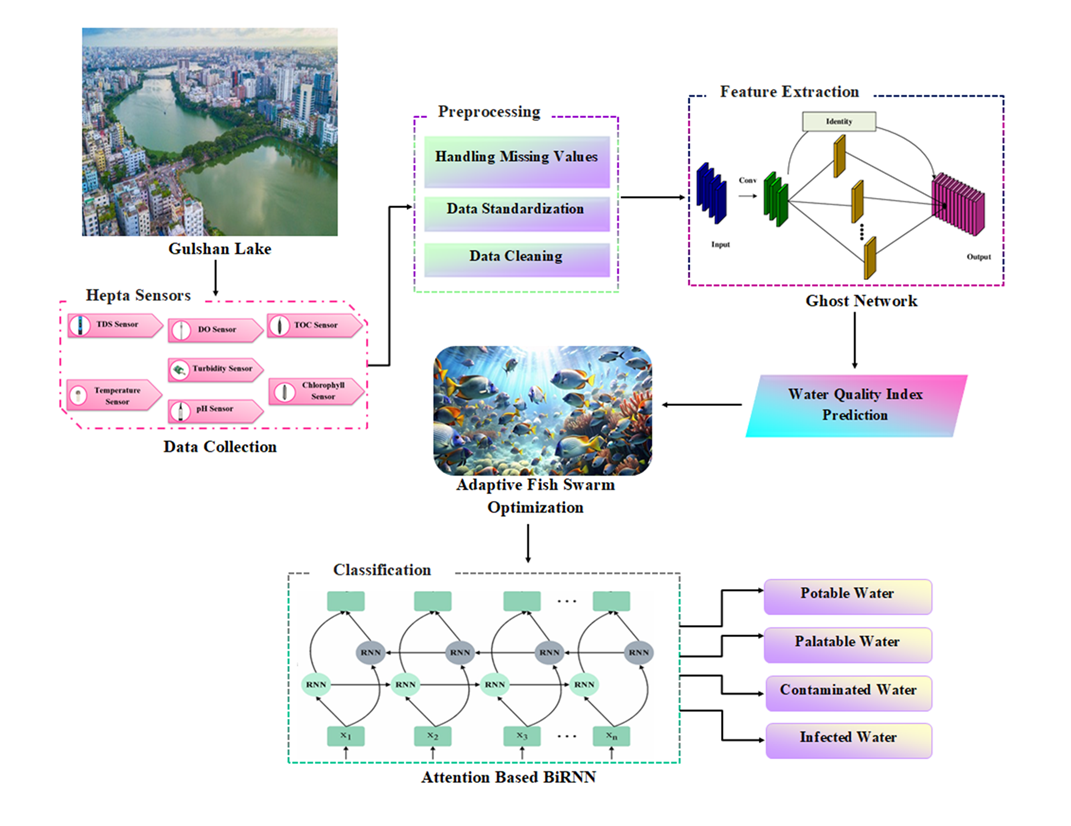
Water Quality Prediction (WQP) plays an essential role in supplying high-quality water to diverse sectors which is dominant for every living organism in the environment. WQP is an important issue that affects both the sustainability of ecosystems and the health of aquatic species. Traditional techniques for determining the quality of water are expensive, time-consuming, and prone to errors. To overcome these issues, a novel REmote WAteR Sensing for quality assessment (REWAR-Sense) methodology is proposed to develop an automated system for the prediction and classification of water quality in Gulshan Lake. Initially, the raw Water Quality (WQ) parameters were gathered from the Gulshan Lake using Hepta sensors and stored them into the ThinkSpeak Cloud for centralized data collection. These gathered data are fed to the preprocessing module to standardize the data. A Deep Learning (DL) Network is employed for feature extraction that identifies the critical patterns of WQ and reduces the data complexity. After feature extraction, a Water Quality Index (WQI) is predicted using an adaptive metaheuristic optimization algorithm that provides a numerical score to indicate the water's condition of the Gulshan Lake. Finally, an attention-based neural network categorizes the WQ into four such categories to enhance the Water Resource Management (WRM) for efficient environmental monitoring. The REWAR-Sense methodology was simulated by using MATLAB and it is validated by Gulshan Lake Dataset. The REWAR-Sense methodology is evaluated based on a number of variables such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. In comparison, the proposed REWAR-Sense method achieves an accuracy of 93.45%, precision of 92.80%, recall of 93.20%, and F1-score of 93.00% outperforming the existing AutoDL, SOD-VGG-LSTM, and LSTM-CN methods respectively.