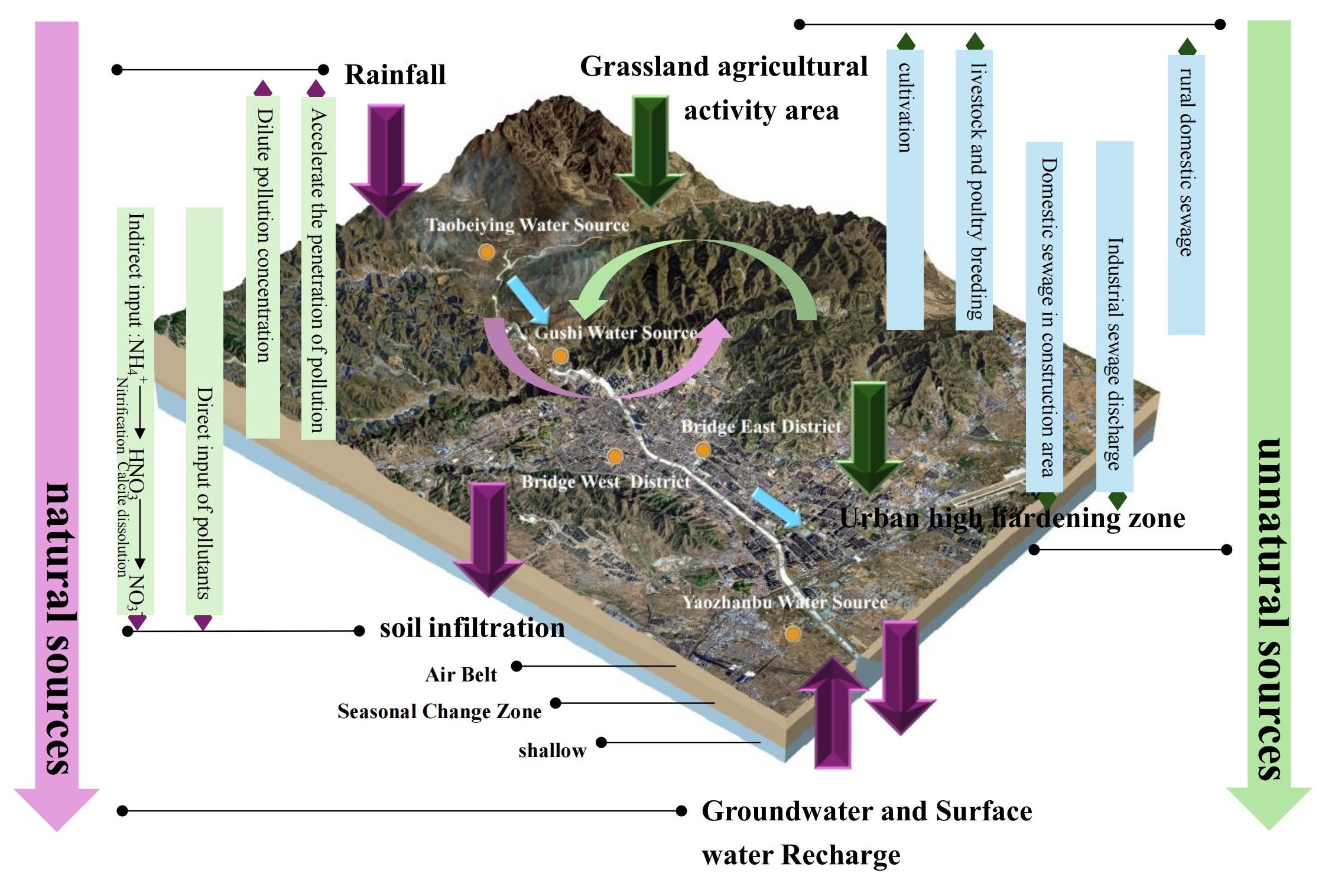
In order to investigate the main pollution factors of underground drinking water sources in semi-arid agricultural areas in China, and to reveal the threatening influence of pollutants on the normal water security of local society. Single-factor evaluation index, principal component analysis, basic data statistics are used to clarify the main pollution indicators of underground drinking water sources in Zhangjiakou main city and discuss the main influencing factors of the change of their pollution concentration, and evaluate the degree of health threat of its pollution to the drinking water of local residents. The results show that: the water sources of Taobeiying and Gushi are deeply affected by human activities, and nitrate, as the only exceeding substance under drinking water standards, is the most important indicator of groundwater pollution; and the nitrate con-centration of groundwater is higher in the pasture and nearby agricultural activities; nitrate contamination levels in groundwater are within the health acceptability range for the vast majority of the population, with only newborns in the Taobeiying drinking water source being exposed to a non-carcinogenic risk of nitrate. The results of the study will help to maintain a stable groundwater environment.
Total file downloads: 35