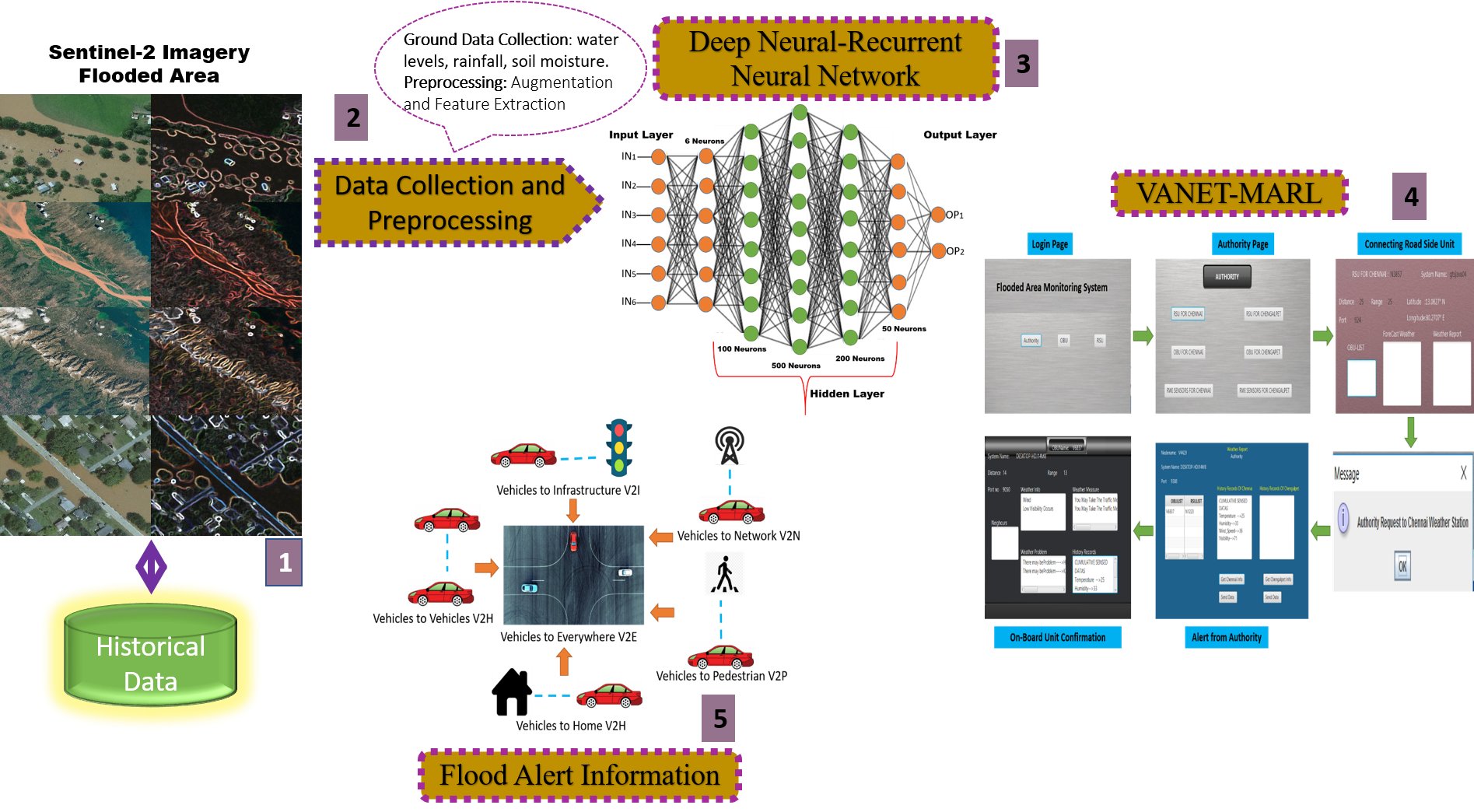
Floods are a major contributor to the destruction of infrastructure and the overall economy of afflicted countries, leading to loss of life and significant damage. Remote sensing, satellite imagery photography, global positioning system, and geographic information system (GIS) are commonly used to identify floods and analyze the associated damages. The research presented here integrates Sentinel-2 satellite images, VANET with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL), and a deep neural RNN for early flood prediction. Sentinel-2 imaging delivers extensive geographical and temporal data regarding land cover and water bodies, while VANET-MARL provides real-time ground-truth information and distributed decision-making capabilities. The Deep Neural RNN efficiently acquires intricate patterns from the combined data to forecast the likelihood, intensity, and scope of floods. The experimental findings clearly show that the suggested system outperforms standard methods in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and lead time. VANET-MARL integration improves the system's ability to adapt and remain strong in changing circumstances. The results showed that the method was 94.8% accurate in early predicting floods.
Total file downloads: 32