- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 26 Downloads
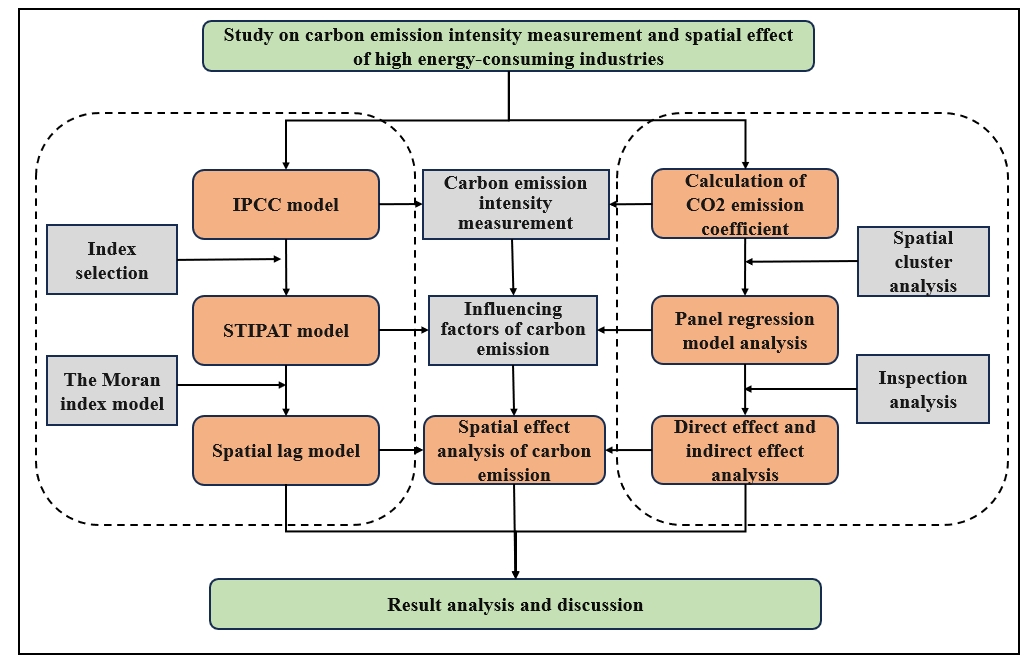
High energy consumption industry is an important source of carbon dioxide emissions, and reducing pollution and carbon is an important measure for China to achieve the goal of "2030 carbon peak 2060 carbon neutral". Based on the improvement of the traditional calculation method of IPCC carbon emission intensity, this paper measures the carbon emission intensity, selects the data of high energy consuming industries in 30 provinces in China from 1997 to 2022 as samples, uses the stipat model and Moran index to analyze the correlation of the influencing factors of carbon emission, and uses the spatial measurement model to study the spatial effect of carbon emission intensity. The results show that: first, the overall carbon emission intensity of high energy consuming industries shows a downward trend, with typical spatial heterogeneity. During the sample period, the carbon emission intensity of high energy consuming industries in 30 provinces in China was calculated based on the IPPC method, with the overall decline. Second, the carbon emission intensity of high energy consuming industries has significant spatial autocorrelation characteristics. According to the global Moran index, the center of gravity moves from east to West as a whole. Third, the carbon emission intensity of high energy consuming industries is affected by multiple environmental factors. Industrial structure (INS), regional gross domestic product (GDP) and regional economic development (ECO) have a significant impact. Fourth, the carbon emission intensity of high energy consuming industries has a significant spatial spillover effect. According to the regression results of spatial Dobbin model with double fixed effects, the direct and indirect effects of carbon emission intensity of high energy consuming industries are significant.