- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 90 Downloads
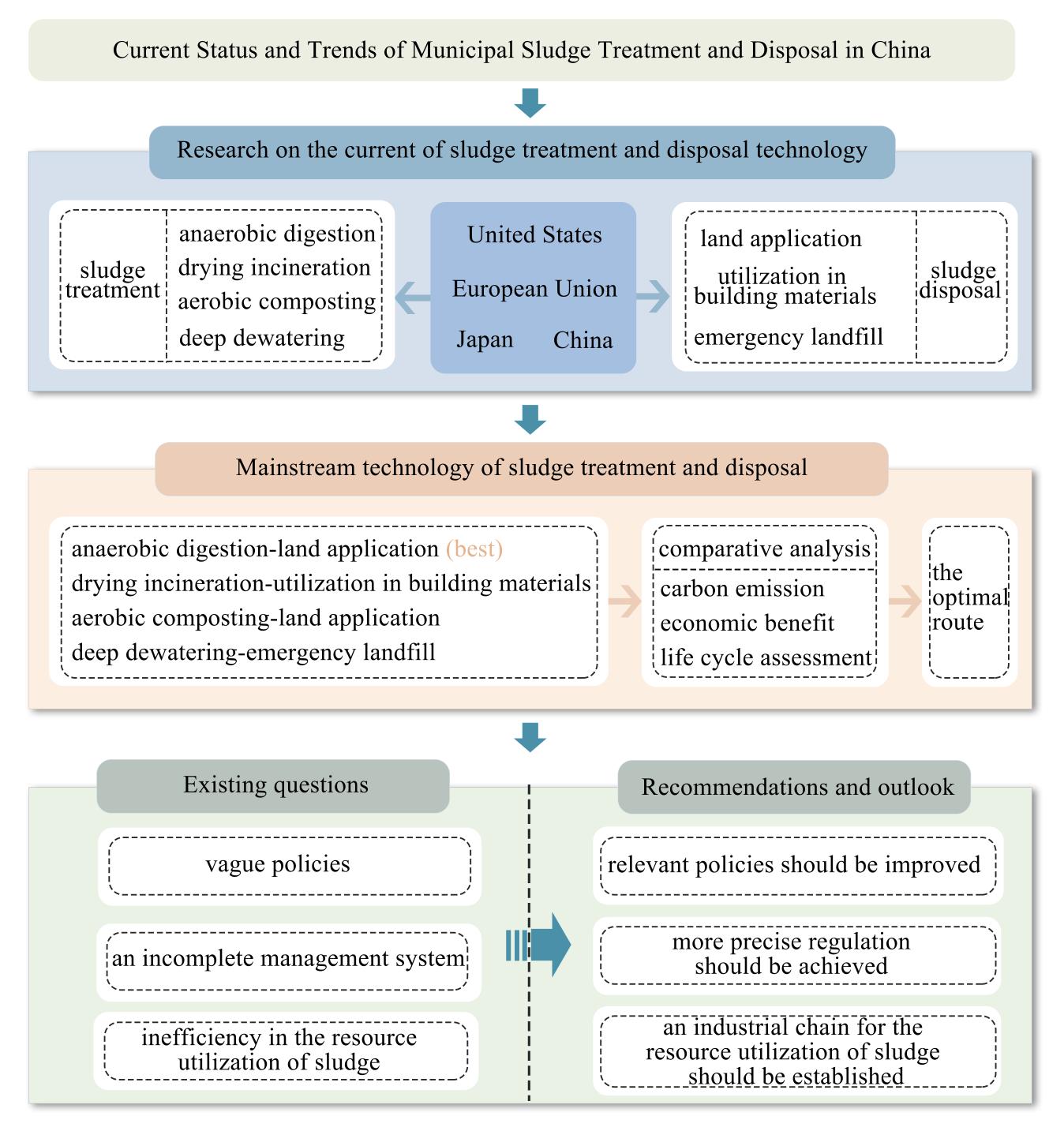
As urbanization accelerates, an increasingly significant problem of municipal sludge treatment and disposal has emerged in China. Sludge is both a waste and a resource, therefore, its reasonable and effective treatment and disposal are crucial for protecting the environment and promoting the recycling of resources. This article reviewed the current status and technologies of sludge treatment and disposal, proposed the mainstream routes for sludge treatment and disposal in China, including anaerobic digestion-land application, drying incineration-construction material utilization, aerobic composting-land application, deep dewatering-emergency landfill. According to the comparative analysis of carbon emission, economic benefit and life cycle assessment, anaerobic digestion-land application was considered the optimal technological route. It has extremely low carbon emissions (-44.43 kg·t-1) (calculated as CO2/dry sludge), low net costs ($31.93/t) and significant environmental benefits, including SO2 (-1.9×105 kg), electricity (-6.2×108 kWh) and fuel (-4.6×107MJ). Based on this, it highlighted the issues in sludge treatment and disposal, such as vague policies, an incomplete management system, and inefficiency in the resource utilization of sludge. In response to these issues, suggestions were made to improve relevant policies, achieve more precise regulation, and establish an industrial chain for the resource utilization of sludge.
In summary, this article offered innovative insights into the optimal technological route for sludge treatment and disposal in China, while highlighting the practical engineering significance of addressing policy, management, and resource utilization challenges. Its recommendations have the potential to drive significant improvements in sludge management practices, contributing to a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable urban environment.