- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 12 Downloads
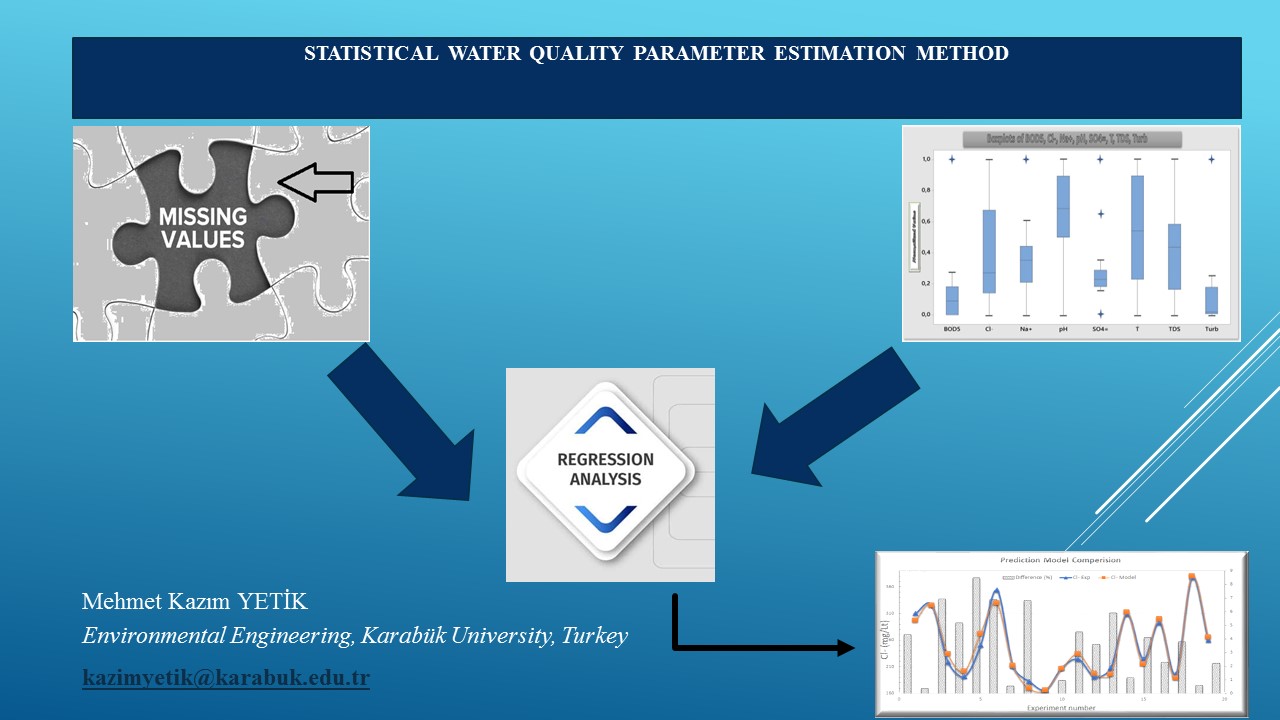
Monitoring water quality parameters in rivers is of critical importance for decision makers and researchers. However, difficulties such as missing data, test values exceeding certain limits and parameters that are not measured but need to be monitored are among the main problems in monitoring water quality. In this study, these three main problems in water quality monitoring processes were addressed and solution-oriented approaches were developed. Solutions were applied for missing and dirty data problems, and multivariate regression and prediction models were proposed for unmeasured parameters. A prediction model was developed using parameters such as BOD5, Cl⁻, Na⁺, pH, SO₄, temperature, TDS and turbidity, and the performance of the model was analyzed in detail for SO₄, Cl⁻, Na⁺ and BOD5 parameters. The accuracy of the model was evaluated with statistical indicators such as MSE, MAPE and correlation coefficient (r). The model showed high accuracy with MAPE values below 10% for most parameters. For example, for the Cl⁻ parameter, MSE was calculated as 118, MAPE as 3.6 and r value as 0.984. In addition, a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) has been developed and used to create an automatic regression model for the Cl⁻ parameter. This system, integrated with VBScripts, has been tested on the Kızılırmak River to prove its applicability within a single program framework for all rivers. The results obtained show the effectiveness and wide-ranging applicability of the proposed method.