- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 19 Downloads
font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;mso-fareast-font-family:Calibri;mso-fareast-theme-font:
minor-latin;mso-ansi-language:EN-IN;mso-fareast-language:EN-US;mso-bidi-language:
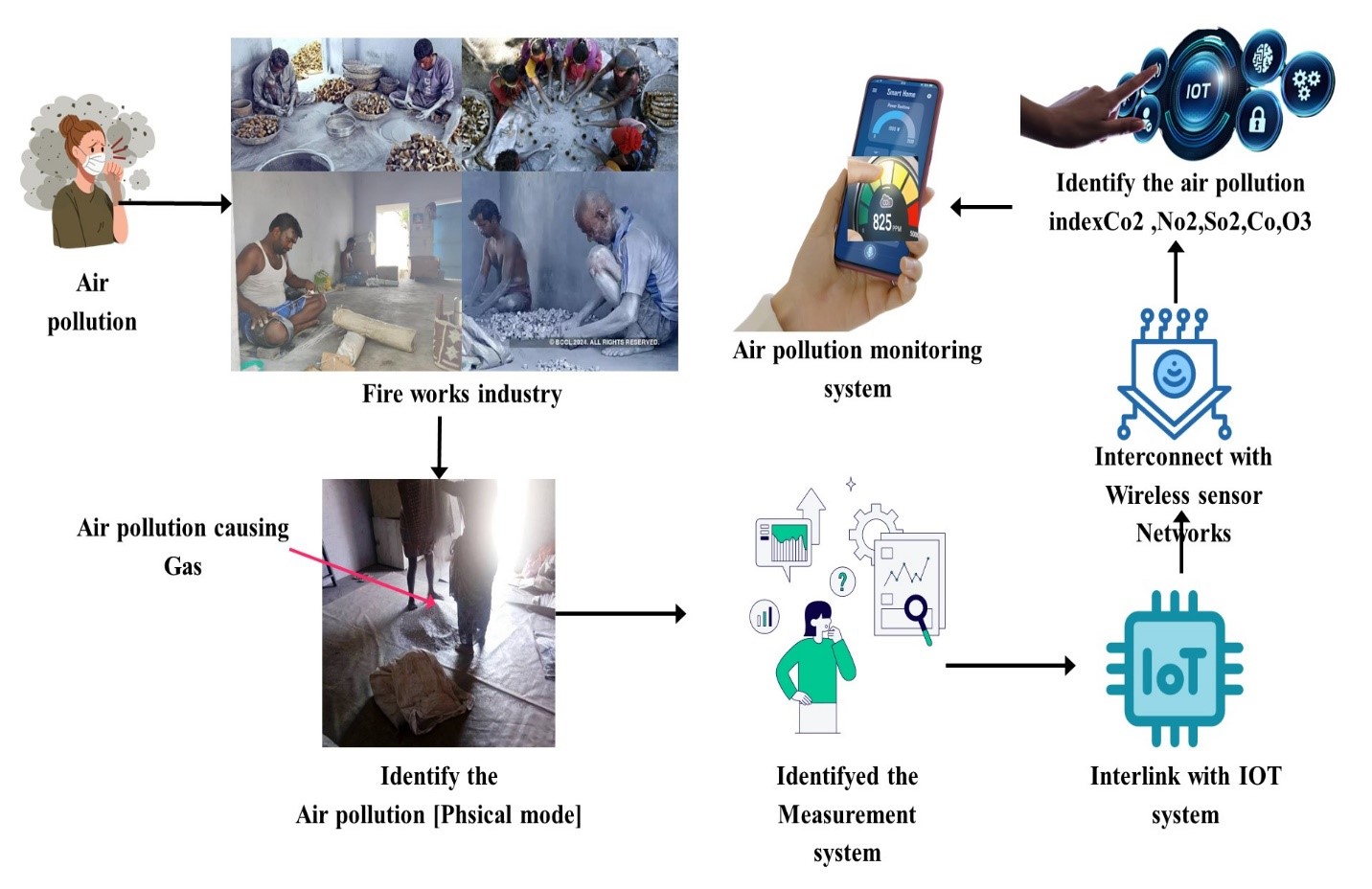
AR-SA">Air is crucial for human survival and a healthy existence, but in modern metropolitan living, it has become a dangerous issue due to its high pollution levels. When weighed against all other businesses, the fireworks sector is extremely dangerous. Every year, air pollution affects many people, including fireworkers, and causes various health problems that can occasionally result in death. Indeed, this work attempted to develop an accurate model for predicting air quality in the United States using a dataset obtained from linked Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Spark model, specifically wireless sensor networks (WSN). In order to predict air pollution caused by the introduction of hazardous substances including SO2, NO2, O3,Particulate matter and CO into the Earth's atmosphere, this study explores the concept of merging the concepts of the Internet of Things. In conclusion, understanding forecast quality requires the computation of assessment measures using the proposed model.
mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin;mso-fareast-font-family:Calibri;mso-fareast-theme-font:
minor-latin;mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;mso-bidi-font-family:"Times New Roman";
mso-bidi-theme-font:minor-bidi;color:#0070C0;mso-ansi-language:EN-IN;
mso-fareast-language:EN-US;mso-bidi-language:AR-SA">
mso-fareast-font-family:Calibri;mso-fareast-theme-font:minor-latin;color:#0070C0;
mso-ansi-language:EN-IN;mso-fareast-language:EN-US;mso-bidi-language:AR-SA">This research work used the RMSE to evaluate our predictions made using the Spark model. Good prediction models should typically have RMSE values of less than 0.3. It is accurate to say that our RMSE is 0.14 < 0.4, which supports the validity of our model.
"Times New Roman",serif;color:#0070C0">
"Times New Roman",serif;color:#0070C0">