- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 64 Downloads
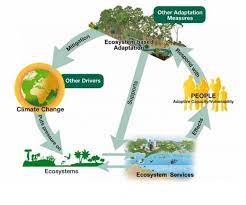
Climate change significantly threatens global ecosystems and human societies, necessitating innovative strategies for mitigation and adaptation. This study addresses the problem of increasing climate vulnerability by investigating the role of ecosystem-based adaptation (EbA) in enhancing resilience across various ecosystems. The research employs a comprehensive review of existing literature, focusing on global case studies and best practices. Key concepts such as ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable land management are analyzed. The proposed methodology includes assessing the effectiveness of EbA measures in mitigating climate impacts on biodiversity, water resources, agriculture, and coastal areas. Additionally, the study examines the socio-economic benefits of these strategies for local communities, livelihoods, and cultural heritage. Policy frameworks and governance structures essential for the broad adoption of EbA at local, national, and international levels are evaluated. Results indicate that EbA measures significantly reduce climate vulnerability, improve ecosystem health, and provide socio-economic benefits, including enhanced livelihoods and cultural preservation. This comprehensive analysis informs policymakers, practitioners, and stakeholders about the importance of integrating natural systems into climate adaptation strategies, promoting sustainable and resilient futures.