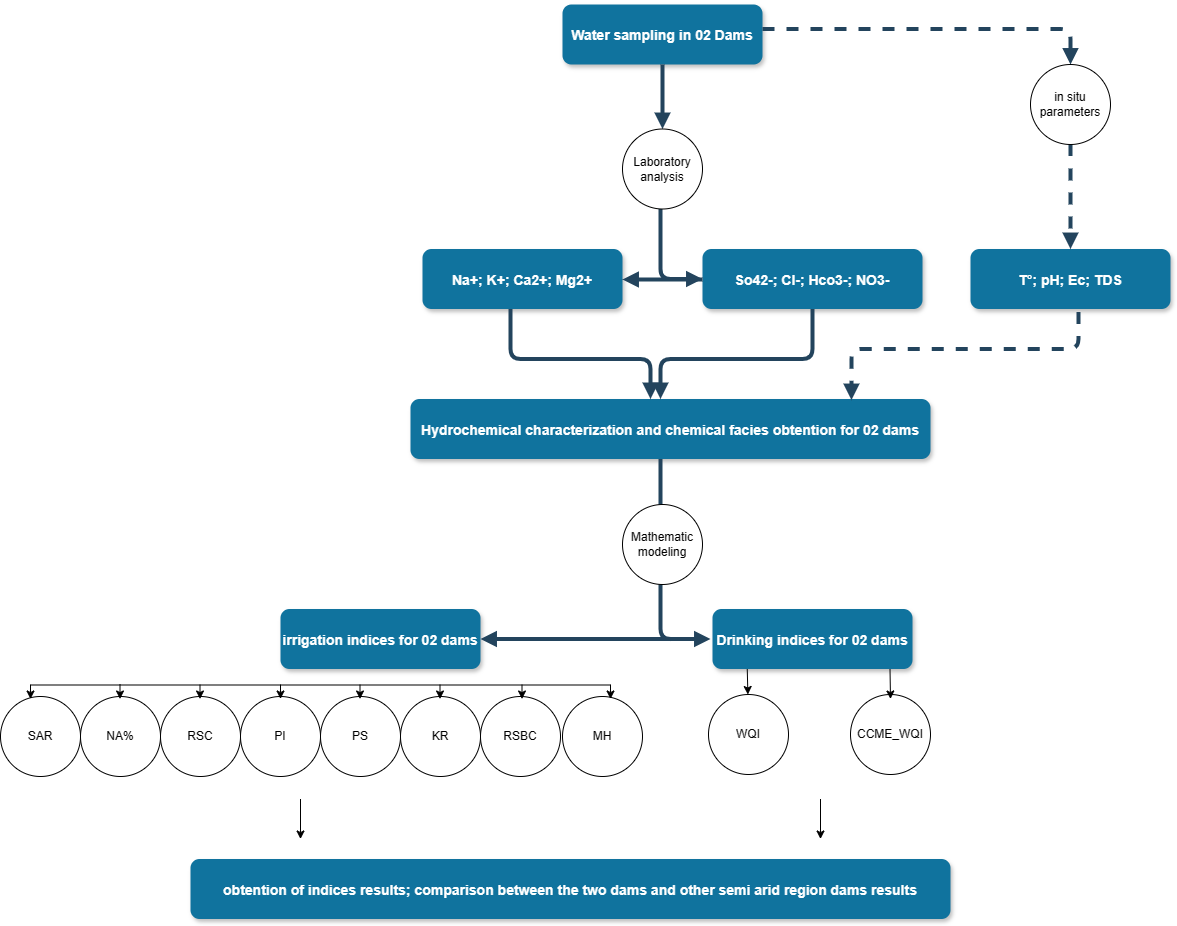
The surface water quality of Timgad and Yabous dams in the semi-arid region of northeast Algeria was evaluated using physicochemical data collected monthly from May 2023 to April 2024. Parameters including temperature (T), pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), chloride (Cl⁻), sulfate (SO₄²⁻), bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻), nitrate (NO₃⁻), sodium (Na⁺), potassium (K⁺), calcium (Ca²⁺), and magnesium (Mg²⁺) were analyzed to assess suitability for drinking and irrigation purposes. For drinking purposes, the Water Quality Index (WQI) and CCME-WQI were employed. Results showed permissible WQI values for Timgad Dam throughout the year, with Yabous Dam exhibiting good quality consistently. However, CCME-WQI classified Timgad Dam as marginal and Yabous Dam as fair annually, indicating a need for caution, particularly for Timgad Dam. For irrigation purposes, various indices including Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR), Sodium Percentage (NA%), Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC), Permeability Index (PI), Potential Salinity (PS), Kelly’s Ratio (KR), Residual Sodium Bicarbonate (RSBC), and Magnesium Hazard (MH) were utilized. While both dams generally demonstrated suitable classes for irrigation, Timgad Dam exhibited unsuitability due to elevated Potential Salinity values, attributed to high chloride and sulfate concentrations that probably come from anthropogenic activities and natural processes, and MH values were unsuitable for both dams throughout the year.
Total file downloads: 63