- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 23 Downloads
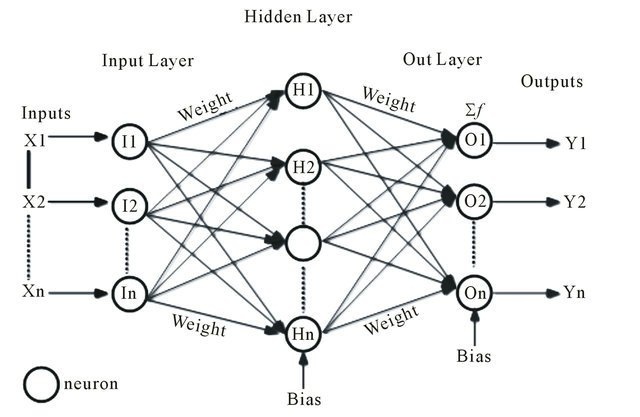
Key features for the quality assertion of geopolymer composites are the vital strength characteristics of geopolymer composites. In this work, an artificial neural network data-driven model was employed for predicting 28-day vital strength characteristics for geopolymer composites incorporated with ingredients such as fly ash, manufactured sand, pond ash, bottom ash, coarse aggregate water, sodium hydroxide, and sodium silicate in diverse combinations. In this paper, the ANN model was created using investigational data, and the developed network was trained to fit inputs and the targeted output. ANN modelling was exploited for the prediction of 70 sets of data comprising a training phase of 80%, a testing phase of 10%, and a validation phase of the leftover 10%. To create an artificial neural network, input six parameters to attain one output. Artificial neural networks best exemplified the responses of individual ingredients in composites and established that an artificial neural network is a prospective methodology for predicting vital strength characteristics. It also found that the precision of the outcome primarily depends on the erudition matrix, and the number of data exploited in the training and testing of the network may have had the highest error from -0.0029 to 0.0034 on evaluation.