- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 18 Downloads
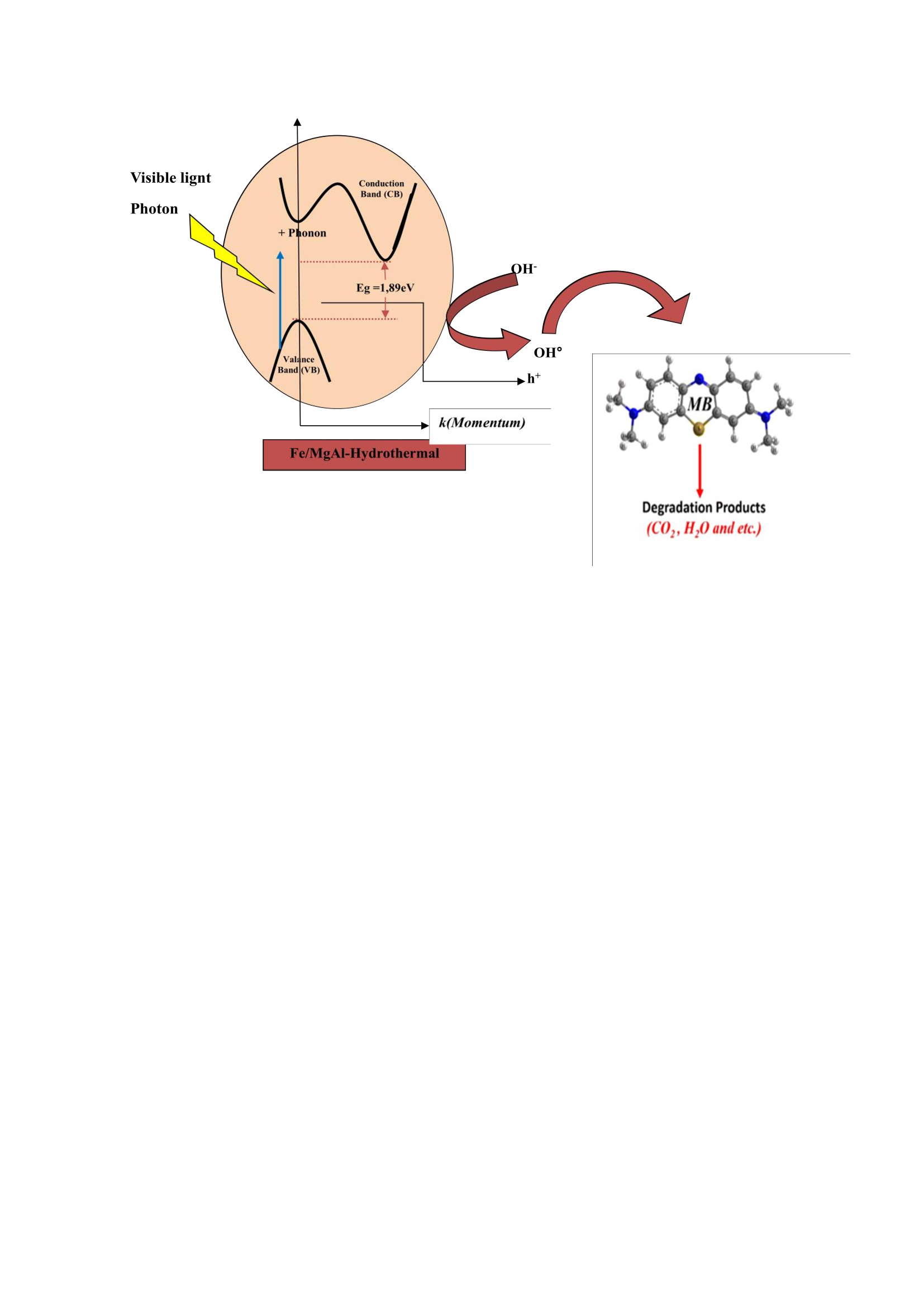
A novel technique involving hydrothermal synthesis was employed to prepare nanocomposite precursors of lamellar double hydroxide based basic mixed oxides. This method extended ongoing research on iron-impregnated hydrotalcite-supported nanomaterials. The iron-based Fe/MgAl-h nanocomposite was prepared via dry impregnation, introducing a known % by weight of Fe (NO3)3.9H2O metal salt into the hydrothermally synthesized MgAl-h structure. For comparative analysis, the photocatalytic performance of Fe/MgAl-h was compared with the coprecipitation-synthesized Fe/MgAl-c after calcination at 400°C, using various characterization techniques. Structural examination revealed a double-layered hydroxyl structure and the presence of iron oxide phase Fe2O3 in Fe/MgAl-h400. Optical assessments indicated an indirect band gap energy of 1.89 eV for solid Fe/MgAl-h400, which is suitable for visible light absorption. Photocatalytic experiments for methylene blue (MB) dye degradation in aqueous solution were performed under artificial irradiation with a tungsten lamp as the visible light source, mirroring the conditions of Fe/MgAl-c400. Using 50 mg/L MB concentration and 0.5 g/L catalyst quantity, increased MB removal efficiency with time was observed. A comparative study of hydrothermal and coprecipitation synthesis methods showed decreased photodegradation for the hydrothermally prepared solid. Fe/MgAl-h400 and Fe/MgAl-c400 exhibited reaction efficiencies of approximately 46% and 67%, respectively, possibly attributed to their distinct indirect and direct band gap characteristics. Moreover, a wider band gap in a semiconductor material offers several advantages for the degradation of dyes.