- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 13 Downloads
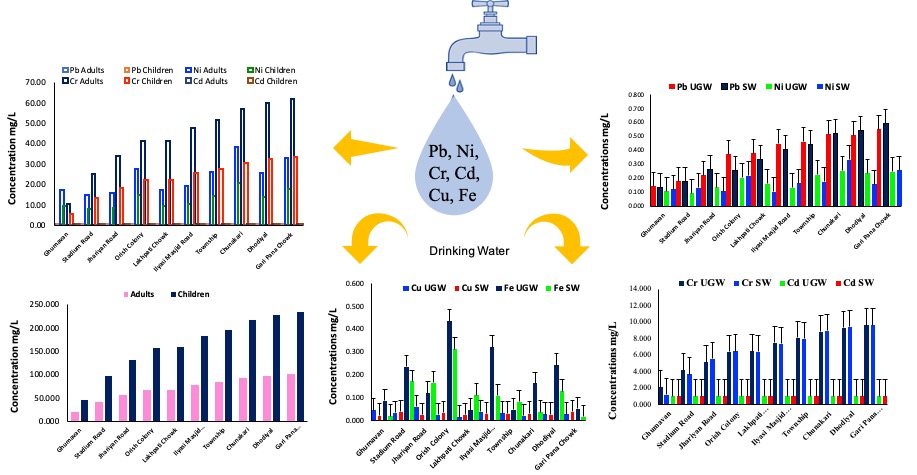
The study was conducted to quantify Pb, Ni, Cr, Cd, Cu, and Fe in drinking water (surface and subsurface water) from Nawanshahr Town, Abbottabad, Pakistan, and to evaluate the associated threat to the health of the inhabitants. An atomic absorption spectrometer (Perkin Elmer, AAS-700) was utilized to quantify the metals and compare them to the threshold level set by Pak EPA. Ni, Pb, Cr, Cd, and Cu levels were higher than Pak-EPA permissible limits, so they were unacceptable. Considering HM level, health risk assessments such as Consumers Daily Intake (CDI), Hazard Quotient (HQ), Health Index (HI), and Targeted Cancer Risk (TCR) were calculated. The order of CDI values in both adults and children was Cr > Cu > Pb > Fe > Ni > Cd and the values of HQ were higher than 1 for all HMs in water samples indicating non-carcinogenic risk to the residents except for Ni. The HI values >1 for all metals of each site indicate adverse non-carcinogenic health effects. Moreover, the results of TCR of all metals were higher in all locations indicating the carcinogenic risk. The present study can be helpful for residents and government officials to take protective measures and reduce contamination of drinking water with heavy metals.