- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 20 Downloads
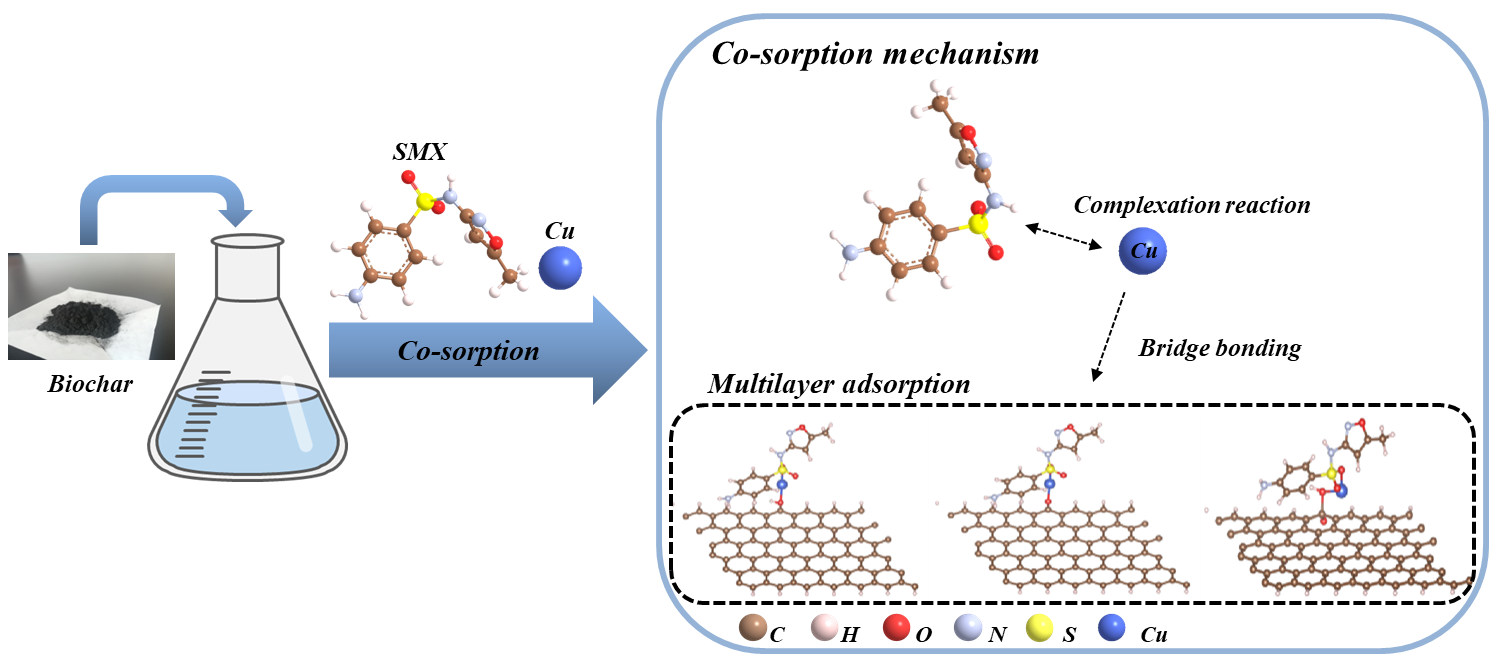
Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and copper (Cu) are common antibiotic and heavy metallic contaminants. They can be removed separately through biochar sorption method. However, the interaction between SMX and Cu remains an unresolved issue in the sorption process of biochar. In this paper, two biochar samples were prepared from maize straw at temperatures of 300 ℃ and 600 ℃. The interaction between SMX and Cu in the sorption process on biochar was investigated using the batch equilibrium experiment method and quantum chemical calculations. The results showed that co-existing of SMX and Cu has a significant contribution to each other’s sorption on biochar. In the coexisting system of SMX and Cu, the sorption capacity of HBC600 for SMX and Cu were 24.22 mg/g and 96.23 mg/g, which were higher than the single system. Quantum chemical calculations showed that due to the bridge bonding and complexation of Cu and SMX on the biochar, the biochar may have formed OH-Cu-SMX, CO-Cu-SMX and COOH-Cu-SMX bonds with the pollutants in the mixed system, and the sorption energy was significantly increased. This indicates that the sorption capacity of biochar for both pollutants was enhanced in the mixed system.