- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 20 Downloads
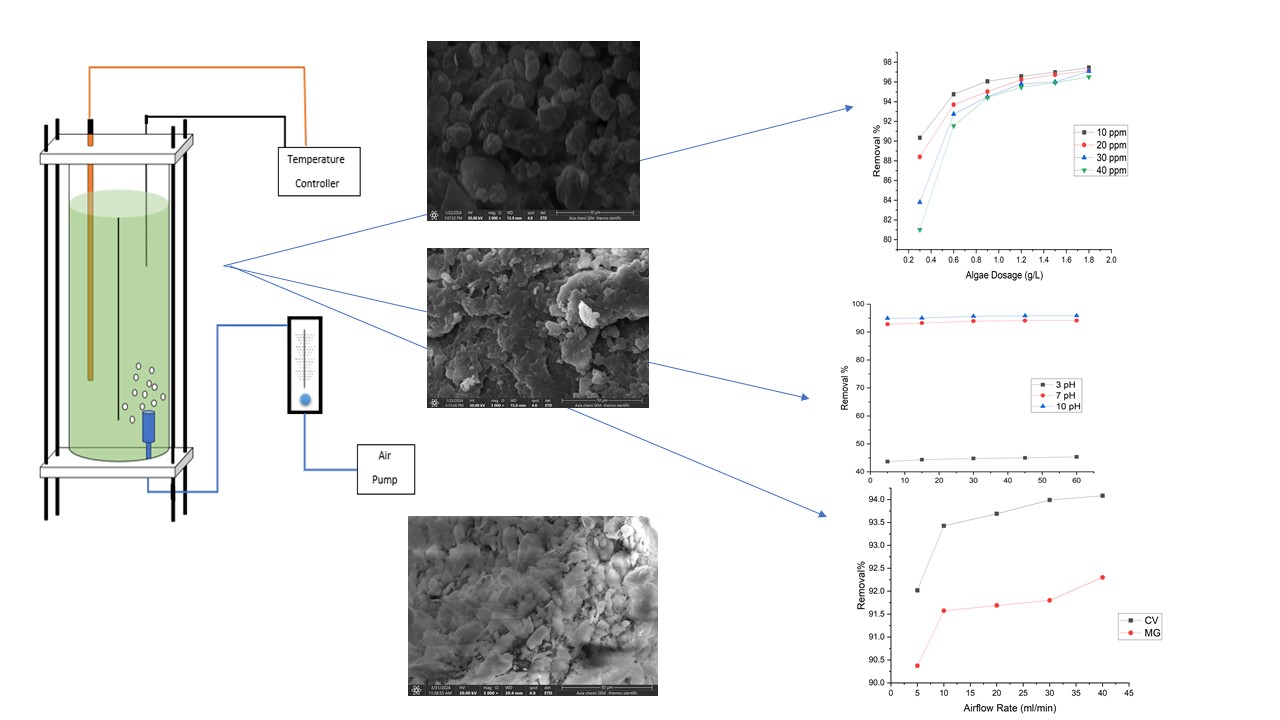
Malachite green (MG) and Crystal Violet (CV) are used mainly as dyestuff and antimicrobials in aquaculture. They have a severe toxic effect on the environment. Several techniques were used to remove impurities from an aqueous solution: chemical, physical, and electrical. Among all these techniques, using dry algae is a more economical and helpful process. This study aims to investigate using an airlift reactor in the removal of MG and CV by chlorella algae as a biosorbent under different variables. The experiments were carried out in an airlift bioreactor. The experiments were carried out under the effect different operating conditions of initial dye concentration (5-40 ppm), alga dosage (0.3-1.8 gm/l), pH (3–10), air flow rate (0-40 ml/min), temperature (298-318 K) and contact time (5-60 min). The results show that the introduce of air bubbles significantly enhances the removal efficiency of the dye. The best removal effectiveness was 95.2% for MG dye and 96.1% for CV dye. The thermodynamics results reveal that the processes are exothermic for both dyes. Kinetic and adsorption isotherms results show the best fit is pseudo-second order and Langmuir model. The mass model result shows that the liquid film diffusion model was the best-fitted for both dyes.