- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 34 Downloads
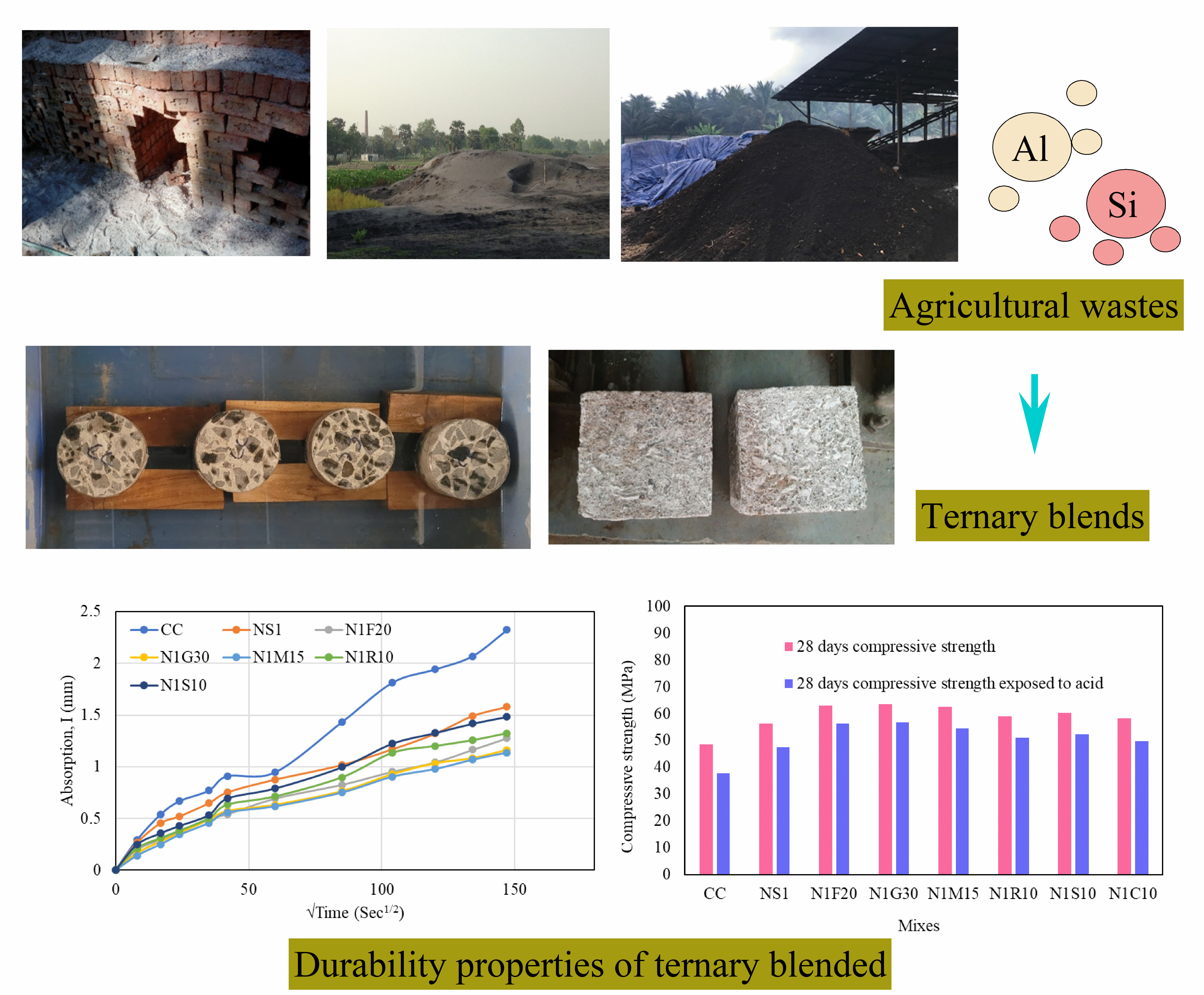
The demand for sustainable concrete in civil infrastructure operations grows by the day, resulting in the use of agricultural and industrial byproducts and controlling high-cost nanomaterials. Ternary blended concrete is an excellent alternative to conventional concrete for long-term development by lowering carbon footprint. Ternary blended concrete is a green and sustainable concrete made from three separate source components to make a binder. The fundamental benefit of ternary mixed concrete is its densely packed particles of various shapes and sizes, resulting in superior characteristics. This study discusses experimental studies that were conducted to assess the durability properties of regular ordinary Portland cement (OPC) concrete and ternary blended concrete containing 1% nano-SiO2 and industrial or agricultural byproducts. Concrete durability is defined as its capacity to sustain a safe degree of serviceability and various environmental exposure circumstances without requiring considerable repair or rehabilitation during its service life. Conventional concrete is prone to cracking because of its low tensile and durability properties. Six potential mixes were investigated in this work: three blends based on industrial byproducts (fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag, and metakaolin) and three mixes based on agricultural byproducts (rice husk ash, corncob ash, and sugarcane bagasse ash). This study investigated the durability characteristics such as water permeability, sorptivity, resistance to sulphate, acid attack, and alkaline attack. The experimental test findings were determined to be well within limitations when compared to the requirements specified in the standard/literature. The study also shows that ternary blended concrete with regulated nano-SiO2 enhances durability metrics significantly. Furthermore, energy dispersive spectrophotometry (EDS) measurements show dense phases with high proportions of Si atoms in the substrate's penetration layer. As a result, ternary mixed concrete is strongly advised in structural repair works.