You are here
Development of sustainable masonry solid blocks by the incorporation of industrial and agro waste.
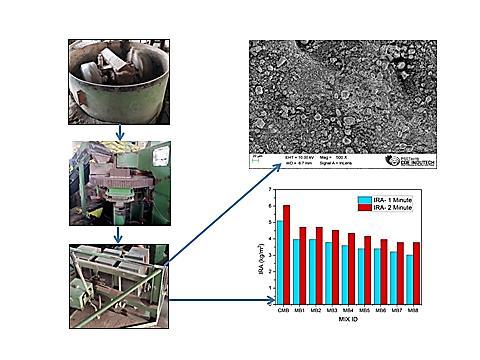
Bricks have been extensively adopted for centuries and continue to play a vital role in the construction industry. Nevertheless of its dependable workability and accessibility, fired clay brick production has been recognized for its comparatively high energy and resource requirements. Traditional clay bricks, widely used in construction for centuries, pose significant environmental challenges. The extraction of clay for brick production can result in habitat destruction and landscape alteration. The firing process in brick kilns consumes substantial amounts of energy, often derived from non-renewable sources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. The development of sustainable masonry solid blocks signifies a revolutionary change in the construction sector, providing a sustainable substitute for conventional building materials. These blocks, typically made from reused or locally obtained materials, demonstrate a dedication to environmental stewardship and the efficient use of resources. This innovative idea of utilizing some industrial waste such as fly ash, bagasse ash, marble dust and stone dust in solid block manufacture significantly reduces the environmental pollution problem, offers an alternative construction material source, and makes the solid blocks economical. Different types of trail mixes have been developed, and the produced masonry solid blocks underwent a series of experimental investigations. The solid bricks are being compared to conventional cement blocks. The developed sustainable solid block (MB6) exhibits a strength that is 43.78% greater than that of conventional cement solid blocks. The present study attempts to determine the optimal material proportion for innovative solid block production. Key words: Carbon footprint, Eco-friendly building blocks, Bagasse ash, Marble dust and Industrial waste
