You are here
Sustainable bio-oil from banana peel waste biomass: Optimization study and effect of thermal drying
Pages :
-
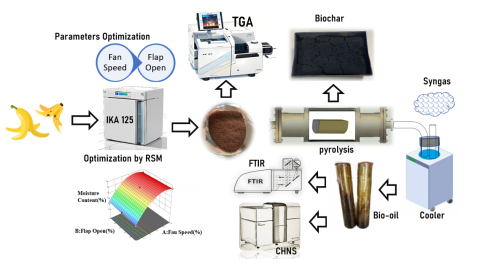
Banana waste has a high level of volatile matter, making it a promising feedstock for pyrolysis in bio-oil generation. Thus, an oven drying method optimization study was conducted to find the drying process of Saba banana peel on flap opening and fan speed. Based on the ANOVA results, it was found that the drying process using 60% fan speed and 40% flap opening for 6 hours of drying time could remove 84.07% of the moisture content from the banana peel. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) was employed to characterize dried banana peels. The TGA study showed that the volatile matter concentration of the dried banana peels was 76.47% when using the ASTM drying method and 70.95% when using the improvement parameter optimization for the drying process. The bio-oil's high heating value (HHV) at 300 °C was 38.88 MJ/kg. The yields of bio-oil, biochar, and syngas obtained from the pyrolysis process were 16.6%, 36.45%, and 46.96%, respectively. The carbon hydrogen nitrogen sulfur (CHNS) ultimate analysis study showed a bio-oil elemental composition of 65.59% carbon, 8.27% hydrogen, 2.94% nitrogen, 0.93% sulfur, and 22.27% oxygen. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy showed that functional groups including alcohol, alkane, phenol, and primary alcohol are present.
